Exploring Innovative Alternatives to Fiber Cement Soffit Boards for Modern Construction
In the ever-evolving landscape of modern construction, the quest for
innovative materials has led to the exploration of alternatives
to traditional Fiber Cement Soffit Boards. These boards, known for their durability and versatility,
have long been a go-to choice for architects and builders. However, with growing environmental concerns
and the demand for sustainable practices, there is a pressing need to reconsider our options.
This blog will delve into various innovative alternatives that not only meet aesthetic and
functional criteria but also align with ecological values. By examining the potential of
materials such as aluminum, PVC, and engineered wood products, we aim to provide insights that can guide
construction professionals in making informed choices that enhance both the performance and
sustainability of their projects. Join us as we explore these cutting-edge solutions that could redefine
our approach to soffit applications in contemporary architecture.

Exploring Sustainable Materials for Soffit Boards in Modern Design
As the construction industry increasingly prioritizes sustainability, the exploration of innovative materials for soffit boards has gained significant attention. Traditional fiber cement panels, though durable, often come with environmental challenges due to their production processes and raw materials. According to a report from the World Green Building Council, the construction sector is responsible for approximately 39% of global carbon emissions, prompting a shift towards more sustainable alternatives. Eco-friendly options such as bamboo, recycled plastics, and reclaimed wood are emerging as viable substitutes that not only reduce carbon footprints but also provide aesthetic value in modern design.
Bamboo, in particular, stands out as a renewable resource with impressive durability, experiencing growth rates surpassing those of conventional timber. Industry research indicates that bamboo can yield up to 25% more bamboo per acre than wood, making it a more sustainable choice for soffit boards. Similarly, the use of recycled plastics not only diverts waste from landfills but also offers a lightweight and water-resistant alternative perfect for various architectural styles. Integrating these materials into modern construction can lead to a more sustainable building process without compromising quality or design integrity.
Innovative Manufacturing Techniques for Alternative Soffit Solutions
 As the construction industry continues to evolve, innovative manufacturing techniques are paving the way for alternative soffit solutions that challenge the dominance of traditional fiber cement boards. One promising direction is the use of advanced composite materials, which combine the lightweight benefits of polymers with the durability of traditional building materials. These composites can be engineered to mimic the aesthetic appeal of fiber cement while offering enhanced resistance to moisture, rot, and pests. Such properties not only extend the lifespan of soffit installations but also reduce maintenance costs for building owners.
As the construction industry continues to evolve, innovative manufacturing techniques are paving the way for alternative soffit solutions that challenge the dominance of traditional fiber cement boards. One promising direction is the use of advanced composite materials, which combine the lightweight benefits of polymers with the durability of traditional building materials. These composites can be engineered to mimic the aesthetic appeal of fiber cement while offering enhanced resistance to moisture, rot, and pests. Such properties not only extend the lifespan of soffit installations but also reduce maintenance costs for building owners.
Another exciting area of development is 3D printing technology, which allows for bespoke soffit designs that are both functional and visually striking. By leveraging additive manufacturing, builders can create complex shapes and patterns that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with conventional materials. This customization not only enhances the architectural appeal of a structure but also opens up new avenues for energy efficiency by integrating insulation directly into the soffit design. As these innovative manufacturing techniques gain traction, they are set to redefine modern construction and offer sustainable alternatives to traditional materials.
Comparative Analysis of Cost and Performance: Fiber Cement vs. Alternatives
When assessing building materials for soffit boards, fiber cement has long been a go-to due to its durability and resistance to moisture and pests. However, as modern construction evolves, so too do material innovations. Alternatives like PVC, aluminum, and composite materials are emerging, each presenting unique advantages. For instance, PVC is not only lightweight but also boasts a high resistance to rot and fading, making it a viable option for environmentally conscious builders. In terms of installation, PVC often requires less labor and can result in quicker project timelines.
Cost efficiency is another key consideration in the comparative analysis. While fiber cement may be initially cheaper, ongoing maintenance costs can accumulate over time, especially in regions prone to harsh weather conditions. On the other hand, aluminum soffit boards, though higher in upfront costs, offer longevity and minimal maintenance, translating into savings over the product's lifecycle. This comparative performance analysis suggests that while fiber cement remains a solid choice, exploring the full spectrum of modern alternatives could provide both economic and practical benefits for contemporary construction projects.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Alternative Soffit Materials
In modern construction, there is a growing trend towards innovative alternatives to traditional fiber cement soffit boards. One notable case study involved the use of aluminum soffit panels, which were successfully employed in a high-rise residential project. These panels not only provided a sleek, contemporary aesthetic but also enhanced durability and low maintenance requirements. The lightweight nature of aluminum made installation efficient, significantly reducing labor costs.

Another alternative showcased was PVC soffit boards, which appealed to a commercial building project where moisture resistance was crucial. PVC offers the benefit of being rot-proof and easy to clean, making it suitable for environments with high humidity. This project demonstrated how incorporating this material not only improved the building's longevity but also contributed to energy efficiency owing to its thermal insulation properties.
Tips for selecting alternative soffit materials include assessing the environmental impact of the materials, such as their recyclability and energy efficiency during production. Additionally, consider the climate of the installation area to choose materials that will withstand local weather conditions. Aesthetic alignment with the overall design of the building should not be overlooked to ensure a cohesive visual appeal.
Future Trends in Soffit Board Materials for Eco-friendly Construction
As the construction industry increasingly prioritizes
sustainability,
innovative alternatives to traditional fiber cement soffit boards are emerging.
These new materials are not only designed to improve the aesthetic and functional
aspects of buildings but also to minimize the environmental impact. One promising
trend is the use of reclaimed wood
and composite materials that combine natural fibers with recycled plastics. This
approach not only reduces waste but also allows for a wide variety of textures and
finishes, appealing to modern architectural styles.
Another noteworthy trend is the rise of biocomposite materials.
Made from natural fibers such as hemp, flax, or bamboo,
these materials provide a lightweight and durable option while maintaining eco-friendliness.
Incorporating additives to enhance moisture resistance and UV stability can further expand their
applicability in various climates. As architects and builders explore these innovative solutions,
the future of soffit boards may see a shift toward materials that not only meet regulatory standards
but also support a commitment to eco-conscious construction practices.

Products
About Us
Download
News
Blog
Contact Us
 LEAO®Deco Ceiling
LEAO®Deco Ceiling LEAO® Perforated Ceiling
LEAO® Perforated Ceiling LEAO® Ceiling Board
LEAO® Ceiling Board LEAO® Groove Interior Panel
LEAO® Groove Interior Panel LEAO® Interior Board
LEAO® Interior Board LEAO® Wood Grain Plank
LEAO® Wood Grain Plank LEAO® Grooved Exterior Panel
LEAO® Grooved Exterior Panel LEAO® Weatherboard
LEAO® Weatherboard LEAO® Access Floors
LEAO® Access Floors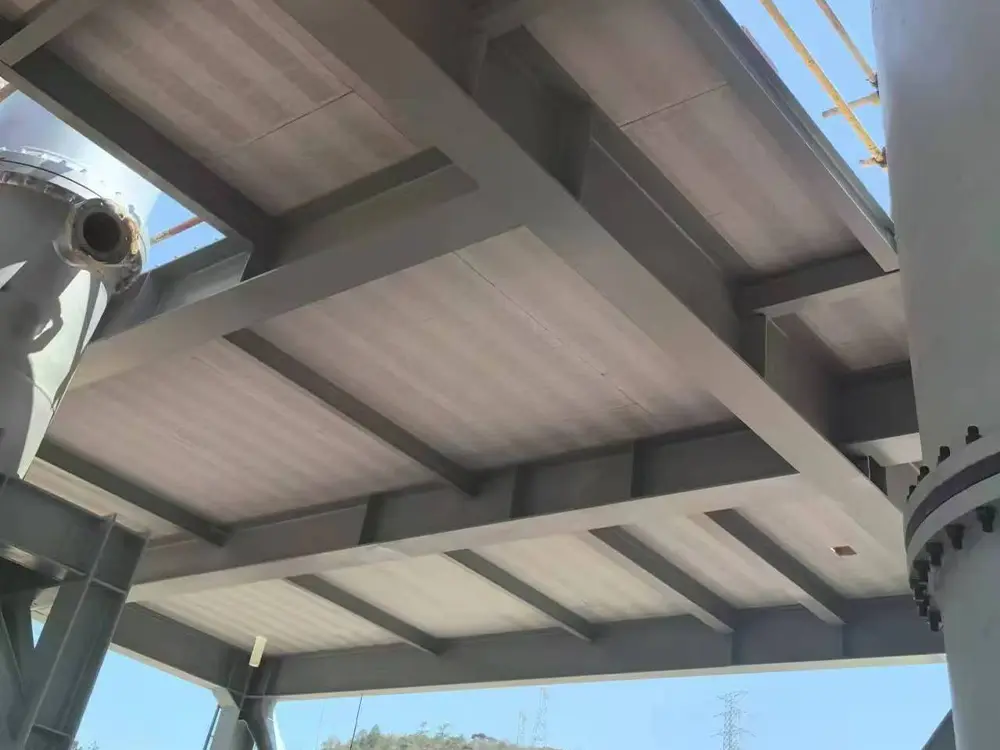 LEAO® Non-removable Formwork
LEAO® Non-removable Formwork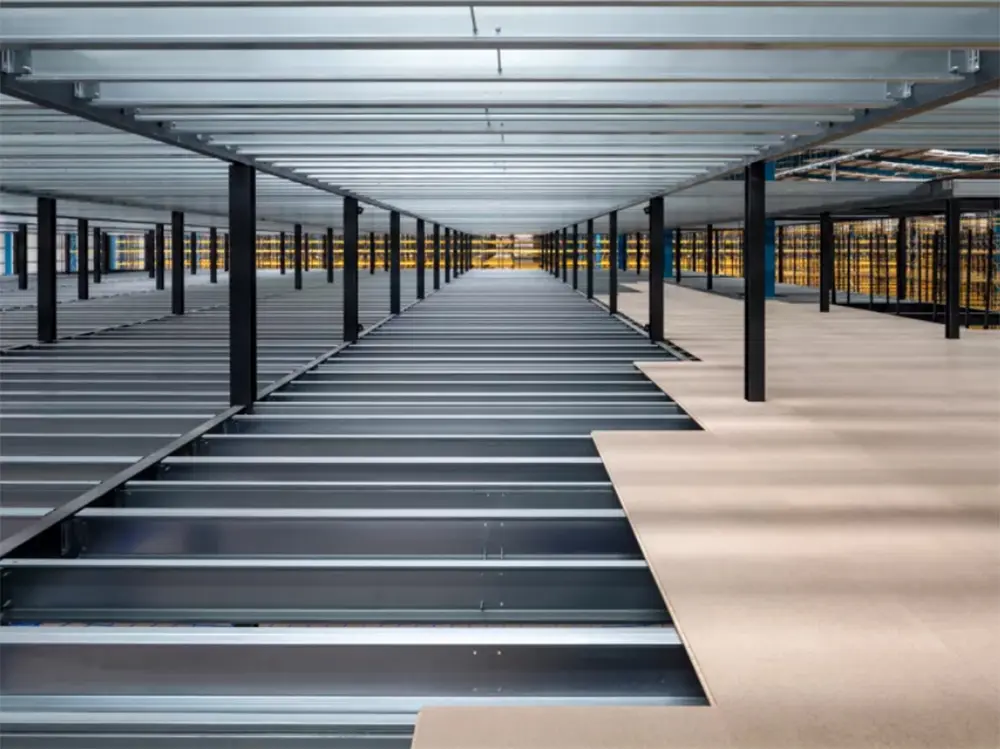 LEAO® Mezzanine Board
LEAO® Mezzanine Board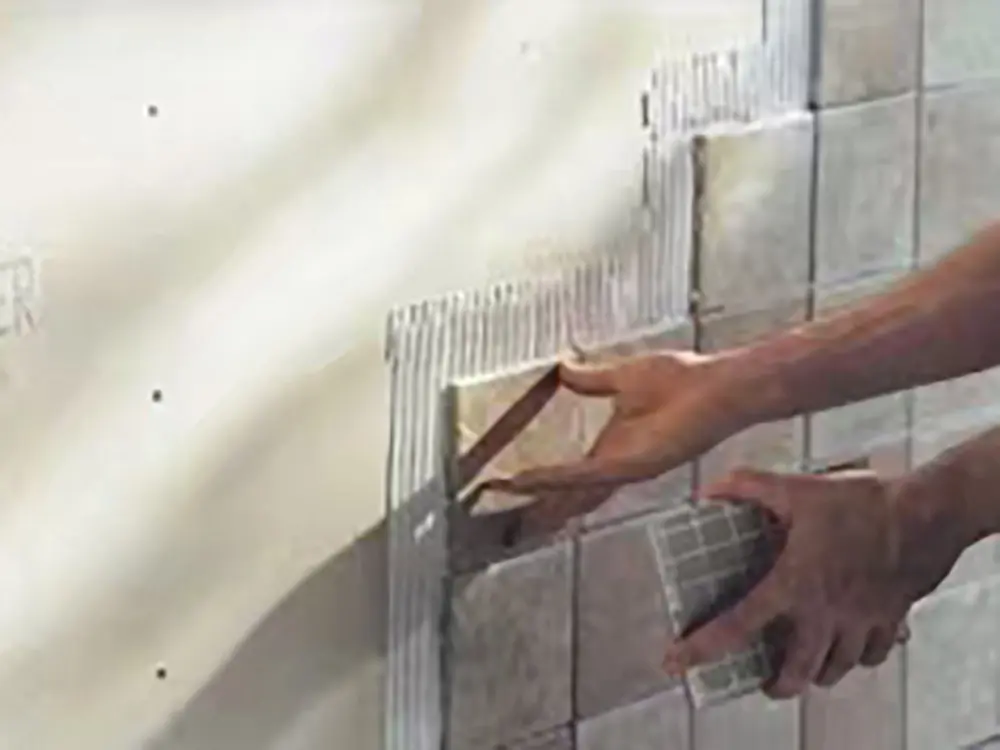 LEAO® Ceramic Tile Underlay
LEAO® Ceramic Tile Underlay LEAO® Floor Plank
LEAO® Floor Plank LEAO® Flooring
LEAO® Flooring LEAO® Wood Style Decorative Panel
LEAO® Wood Style Decorative Panel LEAO® Stone Style Decorative Panel
LEAO® Stone Style Decorative Panel LEAO® Pure Style Decorative Panel
LEAO® Pure Style Decorative Panel
 As the construction industry continues to evolve, innovative manufacturing techniques are paving the way for alternative soffit solutions that challenge the dominance of traditional fiber cement boards. One promising direction is the use of
As the construction industry continues to evolve, innovative manufacturing techniques are paving the way for alternative soffit solutions that challenge the dominance of traditional fiber cement boards. One promising direction is the use of 





